Essential oil is a kind of aromatic concentrated substance obtained from the flowers, leaves, stems, roots, fruits, branches and gums of plants through steam distillation, extrusion, cold soaking or solvent extraction. Essential oils can be divided into diluted compound essential oils and undiluted single essential oils. They have the functions of preventing infectious diseases, antibacterial, antispasmodic, promoting cell metabolism and regeneration, regulating endocrine, etc., so they are widely used in beauty, health care and medicine.

With people's increasing demand for green and healthy life, the potential hazards of heavy metal elements in essential oils have attracted more and more attention. During the plant cultivation process, if the environment or soil is polluted, the residual heavy metal elements may contaminate the plants, resulting in the presence of heavy metals in essential oils. Therefore, it is particularly necessary to study and develop analytical methods for heavy metal elements in essential oils.

In order to detect the content of various heavy metal elements in essential oils, microwave digestion was used for pretreatment and the optimal digestion parameters were optimized. This method has the advantages of high recovery rate and low blank value, which is conducive to the rapid and accurate determination of various inorganic elements in the subsequent process.
Experimental instruments and reagents
Instruments: WMD800 microwave digester, acid remover, laboratory balance, etc.
Reagents: nitric acid (68%), hydrofluoric acid (40%)
Experimental Procedures
●Weigh about 0.5g of essential oil sample (accurate to 0.1mg), add 8mL of nitric acid, and let it stand overnight.
●After adding 2mL of nitric acid, assemble the digestion tank and conduct the experiment according to the set parameters.
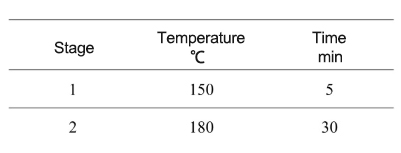
●When experiment finished, wait until it cools down to below 60℃, take out the digestion vessel, open it slowly, and transfer it to the fume hood.
●Place the sample to the heating blocks, heating at 150℃ and dry solution to about 0.5mL, transfer it to a beaker, and dilute it with water.
●If a large amount of white precipitate appears in the solution and the sample cannot be completely dissolved, it needs to be reprocessed.
●Reweigh about 0.5g of the essential oil sample (accurate to 0.1mg) and add 8mL nitric acid.
●Place the digestion tank on the acid remover, pretreat it at 120℃ for about 30 minutes, remove it and cool it after the yellow smoke disappears.
●Add 2mL of hydrofluoric acid, let it stand for about 10 minutes, then assemble the digestion tank and conduct the experiment according to the set parameters.
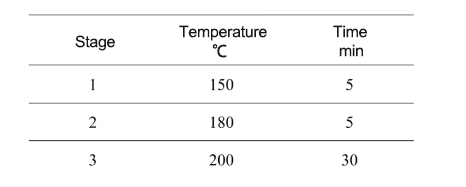
●After the experiment is over, wait until it cools down to below 60℃, take out the digestion tank, open it slowly, and transfer it to the fume hood.
●Place the sample on the heating blocks, heating at 150℃ to about 0.5mL, transfer it to a beaker, add water to dilute, and the sample can be completely dissolved.
●Transfer the solution to a volumetric flask, dilute to the specified volume with deionized water, mix well and set aside.
●Use appropriate analytical instruments to measure the heavy metal content of the sample solution and record the experimental results.

Experimental results
The sample size of the essential oil sample selected in this experiment is about 0.5g. After pretreatment with nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid is added for digestion. The maximum temperature of the experiment is set to 200℃ and kept warm for about 30 minutes. The sample can be completely digested and achieve the expected effect.