Microwave digestion technology is an advanced sample processing method in the field of chemical analysis in recent years. As early as the end of the 20th century, researchers began to use open microwave digestion for wet sample processing. However, this method has some problems, such as volatile acidic components that may cause damage to the equipment and easily lead to element volatilization losses. At the same time, the sample is easily contaminated. In order to solve these problems, researchers developed closed microwave digestion equipment and monitored the digestion process through a sophisticated computer control system, allowing the digestion system to work under high temperature and high pressure conditions, significantly improving digestion efficiency and effectiveness.
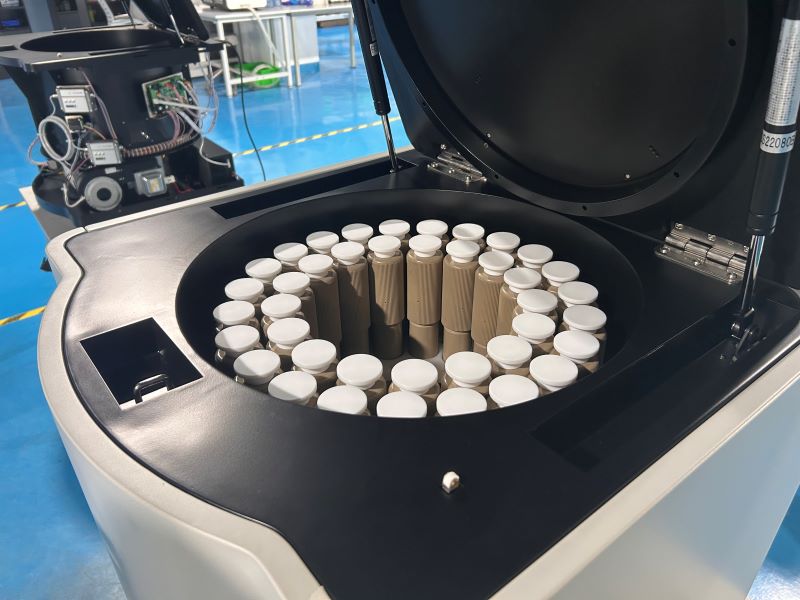

Nowadays, microwave digestion technology has been widely used in sample processing in the fields of textile, food, biology, medicine, metallurgy, etc. This technology not only speeds up the analysis process, but also ensures the accuracy of the measurement results, especially when processing samples containing volatile components, it can greatly improve the measurement accuracy. Through microwave digestion, sample processing is more efficient and accurate, providing strong technical support for various analytical tests.
Microwaves are high-frequency electromagnetic waves with a frequency between 300 and 3000 MHz. Usually, a frequency of 1450 MHz is used in the microwave digestion process. When microwaves encounter different materials during propagation, they will produce reflection, absorption and penetration phenomena according to the material's loss coefficient, specific heat and other characteristics. Unlike traditional heat source heating methods, microwave digestion technology does not gradually heat the sample from the outside, but uses microwaves to heat the sample simultaneously through the inside. During the microwave process, under the action of the alternating magnetic field, polar molecules will alternately arrange in the high-frequency magnetic field, causing the molecules to oscillate at high speed, thereby generating thermal motion and interacting with each other. This oscillation interference allows the molecules to obtain more energy and accelerate the heating process of the sample.

When heated in a closed vessel, microwave digestion not only achieves uniform heating, but also improves digestion results through precise temperature control. Closed microwave digestion technology has significant advantages: on the one hand, required acid volume is very small, usually within 10 mL, and the digestion speed is extremely fast, which can be completed within 16 minutes; On the other hand, the containment system effectively prevents the ingress of contaminants and the loss of elements, ensuring the accuracy of the measurement results. In addition, with the help of computer-controlled technology, the digestion process can be automatically controlled, which further improves the accuracy and efficiency of the operation and ensures the smooth completion of the digestion work.
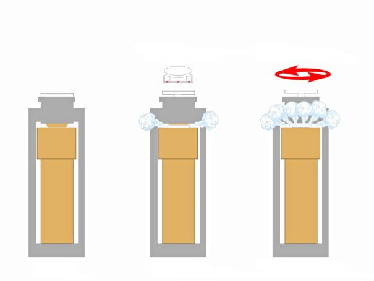
Next, we will explore the application of microwave technology in the field of chemical analysis.
Application in the field of biological sample analysis
In recent years, people have a deeper understanding of the role of trace elements in organisms, especially the detection of heavy metal content in biological samples of traditional Chinese medicine, which is closely related to life safety and physical health. Many countries, especially those that import traditional Chinese medicine, have strengthened relevant control measures and adopted advanced instruments and equipment for detection, such as atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS). However, in these detection processes, incomplete digestion of organic matter in the samples often leads to problems. In order to solve this problem, microwave digestion technology has gradually become an effective solution.
Microwave digestion technology accelerates sample digestion by gradually increasing the pressure of the container in a closed environment and raising the boiling point of the acid. For example, under normal atmospheric pressure, the boiling point of nitric acid is 120°C, but under 5 bars, the boiling point can reach 175°C, significantly improving digestion efficiency. In addition, many heavy metal elements are easy to volatilize, and the use of normal pressure or open digestion methods will lead to loss of elements. Therefore, it is particularly important to choose closed microwave digestion technology, which can effectively improve the reliability and accuracy of digestion.
However, when using microwave digestion technology to treat biological samples, special care must be taken to avoid use of perchloric acid. Perchloric acid has an explosion risk and may react with organic matter during heating to produce chlorine gas. Such reactions will not only lower digestion efficiency, but may also cause excessive pressure in the container, posing a safety hazard. Therefore, during microwave digestion, perchloric acid should be avoided as much as possible to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the digestion operation.
Application in geological environment sample analysis
Microwave digestion technology has shown excellent results in the analytical chemical treatment of geological environment samples. It can efficiently process geological samples and environmental samples and provide accurate data support for related analytical tests.
A、Digestion of geological samples
During the digestion of geological samples, samples such as rocks, soils and minerals are mainly processed. Geological samples usually contain less organic matter, so during the digestion process, the amount of gas (such as CO2) released is relatively low, and the sample volume does not change much, so a large number of samples can be processed. Although the composition of different geological samples varies, most of them contain a certain amount of acid salt components. In order to achieve complete digestion, strong acids such as HF (hydrogen fluoride) are often added. This places high demands on the digestion container.
Since the end of the 20th century, researchers have begun to process geological samples in closed microwave digestion equipment. In order to increase the digestion speed, researchers usually soak the samples in mixed acid, such as HF and HNO3 before digestion, and the soaking time is usually controlled at about 12 hours. Then, the samples are digested by staged heating. Compared with traditional digestion methods, microwave digestion not only improves the processing efficiency, but also greatly reduces the digestion error, ensuring the accuracy of the results. Therefore, in the digestion process of geological samples, microwave digestion technology should be given priority, using HF-HNO3 mixed acid for immersion and gradual digestion to ensure the digestion effect.
B、Digestion of environmental samples
Because of the influence of various factors, environmental samples usually form complex chemical compositions after deposition, including heavy metal elements and organic pesticide residues, which cause serious pollution to the ecological environment. With the continuous advancement of environmental governance and protection work, the demand for environmental analysis and monitoring is increasing, which also puts higher requirements on chemical analysis. However, traditional digestion methods are difficult to effectively digest the organic components in environmental samples and cannot guarantee the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the analysis results.
In this case, microwave digestion technology provides an ideal solution for the treatment of environmental samples. Microwave digestion can effectively improve the digestion effect of organic components and reduce the loss of volatile components by digesting samples in a closed environment with high temperature and high pressure. For example, in the digestion process of soil samples, microwave digestion can fully digest heavy metal components and avoid sample loss and analytical deviations that are common in traditional digestion methods. Through this efficient digestion method, it can ensure that harmful components in environmental samples are thoroughly treated, providing a more accurate basis for environmental pollution monitoring and analysis.

Application in analytical chemistry of metallurgical samples
In the metallurgical industry, chemical analysis of samples is essential for production quality control and raw material testing. As a modern sample pretreatment method, microwave digestion technology is particularly suitable for metallurgical samples that are difficult to handle with traditional digestion methods. By adopting microwave digestion technology, not only can the digestion efficiency be effectively improved, but also the accuracy and consistency of the digestion effect can be ensured.
In the traditional metallurgical sample digestion process, especially for petrochemical product samples, the pressure dissolution method is usually used, and the digestion time is long, usually taking 5 to 8 hours to complete the digestion. Microwave digestion technology significantly shortens the digestion time and can control the digestion time to between 1 and 1.5 hours. This time advantage makes the application of microwave digestion technology particularly prominent in the metallurgical industry, which can improve work efficiency and shorten the sample processing cycle.

Improve chemical analysis results
Microwave digestion technology can provide sufficient heat and pressure in a short time by heating the sample in a closed high-pressure environment to promote the complete dissolution of the components in the sample. Compared with traditional digestion methods, microwave digestion can effectively reduce the loss in the sample and reduce the escape of volatile components. In addition, the high efficiency of microwave digestion can also avoid the generation of harmful gases during the processing process, thereby improving the accuracy of the analysis results.
Application Areas
Microwave digestion technology is widely used in a variety of samples in the metallurgical industry, including ores, alloys, waste materials and petrochemical products. For these samples, traditional digestion methods may not be able to completely digest their complex components, especially the high temperature resistant and corrosion resistant substances in ores and metal alloys. Microwave digestion can effectively break the chemical bonds of these substances, ensuring that all components can fully react in a short time.
Therefore, in the chemical analysis and digestion process of metallurgical samples, microwave digestion technology can greatly improve sample processing efficiency and analysis accuracy, and is an indispensable and important tool for modern metallurgical analysis.

Application in the food industry
With the increasing emphasis on food quality and safety, chemical analysis has become particularly important, especially in terms of heavy metal monitoring, organic pesticide residue monitoring and other component analysis. However, traditional food sample digestion methods are prone to some problems during the processing process, especially organic components in food may generate carbon dioxide (CO₂) and nitric acid reduction products during digestion. These reactions will cause the digestion reaction to produce increased pressure. If not properly controlled, it is very likely to cause safety hazards. In addition, the complex components in some food samples may also be difficult to completely digest, which brings challenges to subsequent chemical analysis.
In order to overcome these problems, microwave digestion technology has shown great advantages in the digestion process of food samples. It can not only effectively control the gas generated during the digestion process and reduce pressure changes, but also improve the digestion effect by optimizing the operation steps to ensure the accuracy of the analysis results.
Gas control and pressure regulation
The fats and organic components in food are prone to generate a large amount of gas during digestion, especially at high temperatures, which may lead to an increase in reaction pressure. Microwave digestion technology can effectively control the release of gas and avoid unnecessary pressure increase by heating the sample in a closed environment. When processing food samples with high fat content, oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) can be appropriately added to not only relieve digestion pressure, but also accelerate the digestion process to ensure that the sample is completely digested.
Improve digestion efficiency and safety
Microwave digestion technology can quickly heat samples in a closed environment of high temperature and pressure, breaking the chemical bonds between organic and inorganic components in the sample, thereby achieving faster and more complete digestion. Compared with traditional digestion methods, microwave digestion technology significantly shortens digestion time, reduces sample loss and contamination risks, and improves digestion effect and safety.
In summary, the application of microwave digestion technology in analytical chemistry has significant advantages. Not only does it reduce acid usage, it also effectively prevents problems such as volatile loss and contamination. Therefore, during the sample digestion process, full attention should be paid to the application of microwave digestion technology. According to the characteristics and needs of specific digestion work, relevant technologies should be rationally selected and applied to give full play to their advantages, thereby improving the efficiency and effectiveness of analytical chemistry operations.