Cell culture is a technique that uses culture media to maintain cell growth and reproduction under in vitro conditions. It is a core tool in the field of modern biological research and technology. In cell culture experiments, we rely on specific culture consumables, among which cell culture containers are particularly important - they are like the "home" of cells, providing an ideal environment for the healthy growth of cells. Correctly selecting different types of cell culture containers can help researchers optimize experimental processes and improve the reliability of experiments.
In this article, Welso will introduce you to several commonly used cell culture containers and their features, and provide suggestions for selecting suitable culture consumables to help you use these in your experiments.

In cell culture, the most commonly used culture containers are cell culture plates, cell culture dishes, cell culture flasks and Erlenmeyer flasks. They have their own features and applications. Next, let's take a look at them one by one.
What materials are cell culture containers made of?
We know that when doing cell culture, we often need to observe the growth status of cells, so the material of the culture container needs to have good optical properties. Commonly used materials are Polypropylene, Polycarbonate and Polystyrene. These material properties can ensure that a safe and observation-friendly culture environment is provided for cells.
Cell culture consumables must be sterile, pyrogen-free, DNase-free, and RNase-free
In cell culture experiments, it is crucial to ensure sterility, enzyme-free and endotoxin-free. Even a small amount of microbial contamination may multiply rapidly, consume nutrients, and even directly cause cell death. Pyrogens and endotoxins are a heat-stable mixture that is seriously harmful to cell proliferation and growth. Endotoxins are lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in the cell walls of Gram-negative bacteria. Even at low concentrations, endotoxins can trigger a strong immune response, leading to cell stress and inflammatory responses, and even inducing cell death. Due to the thermal stability of endotoxins, conventional high-temperature sterilization methods are difficult to completely remove. Therefore, strict endotoxin-free control measures must be taken in cell culture to ensure the purity of the culture environment, thereby maintaining the healthy proliferation and growth of cells. To avoid these adverse effects, all cell culture containers must be tested to ensure sterility, endotoxin-free and pyrogen-free.
Optional culture surfaces
We know that cells are mainly divided into adherent cells and suspension cells. Their growth methods and requirements are different. Therefore, our cell containers need to be surface treated according to the culture methods of these two types of cells.
TC treatment
Conventional surface treatment for the culture of adherent cells is TC treatment, which is the standard surface for the culture of adherent cells. Through special physical surface treatment, polar groups on the surface (such as carboxyl and hydroxyl residues) are combined with the surface material. Surface treatment can change the chemical properties of materials such as polystyrene, converting the originally hydrophobic surface into a hydrophilic surface. This surface polarization helps promote the interaction between the cell membrane and the surface, thereby enhancing the adhesion of the cells, allowing the cells to evenly adhere to the bottom of the container and improving the conditions for cell growth and proliferation.
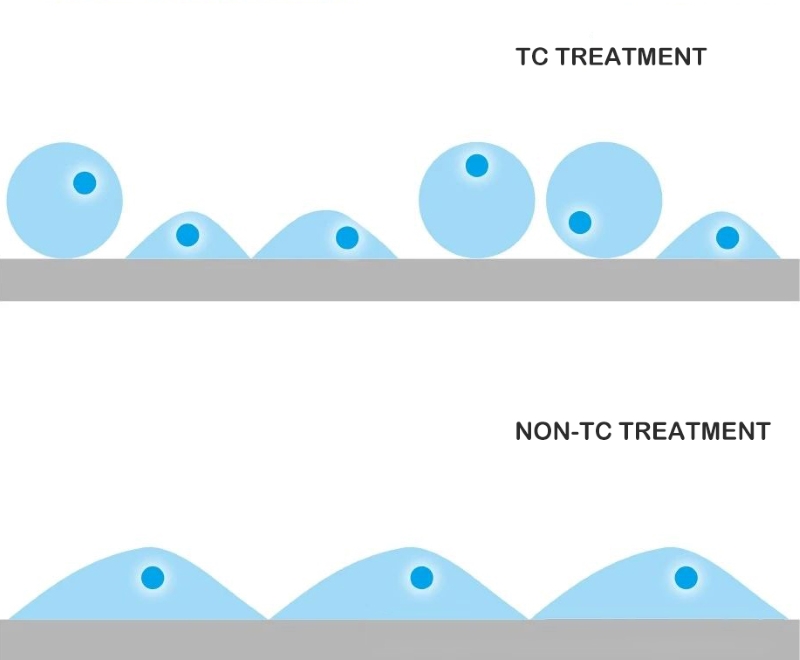
Non-TC treatment
The surface of this culture container maintains the original hydrophobicity of the material and is suitable for suspended cells that can proliferate and grow without adhering to a wall. These cells can suspend freely in the culture medium.
Below we introduce the common cell culture containers.
Cell culture plates
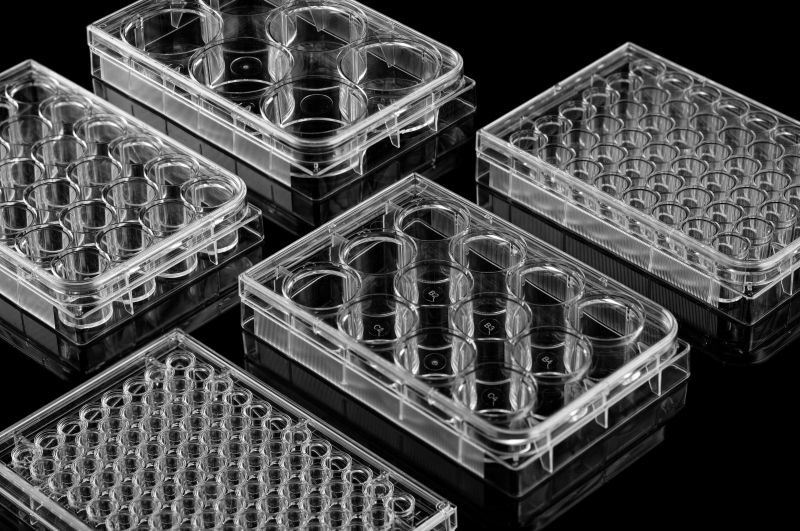

Common specifications include 6-well, 12-well, 24-well, 48-well, and 96-well. Each well is an independent culture space, which facilitates diversified experimental settings.
In order to meet different culture needs and experimental effects, the bottom is available in U and V bottoms. Simply put, the bottom of the U-bottom culture plate has a deeper depression, shaped like the letter U. This design helps to increase the cell contact surface, while the bottom of the V-bottom culture plate has a shallower conical depression, shaped like the letter V. This design helps cell sedimentation.
Two culture plates with different bottom designs need to be selected according to experimental requirements.
Cell culture dishes
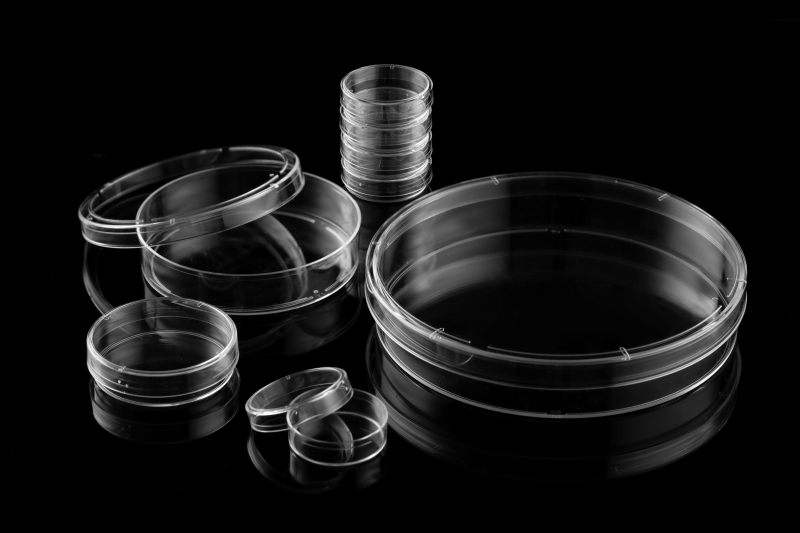

According to the diameter of the culture dish, common specifications include 35 mm, 60 mm, 100 mm and 150mm. Different specifications of cell culture dishes are suitable for different experiments. According to the amount of cells, culture time, and space requirements required for the experiment, choose the appropriate specifications for cell culture. The structural design of the culture dish is simple and convenient, with a breathable cover to allow air to flow more smoothly, and the air in the dish can be exchanged very well. The flat bottom design is suitable for observation under a microscope, so it is particularly commonly used in experiments such as microscope experiments and live cell imaging.
Cell culture flasks
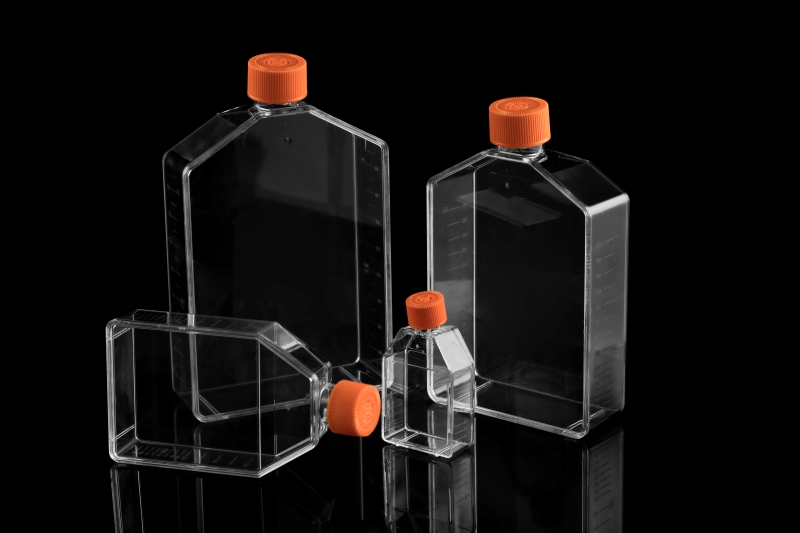

Cell culture flasks are suitable for long-term culture of large-scale adherent cells. The specifications are T25, T75, T175, and T225 with both small and large surface areas . Clear side graduations for easy observation of the volume in the bottle, and the oblique neck design is more conducive to the entry of pipettes or cell scrapers/shovels. The culture flask is equipped with a breathable cover or a sealing cover, and the appropriate gas exchange method can be selected according to the cell type. Its design is also easy to stack, which fully saves incubator space and is an ideal choice for large-scale cell expansion or large-scale sample preparation.
Erlenmeyer flasks
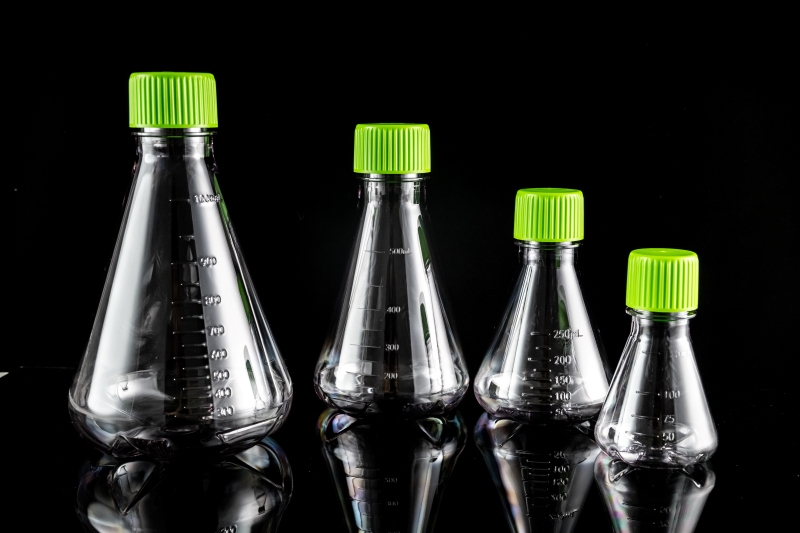

Erlenmeyer flasks are ideal for suspension cell culture, especially for large-scale suspension cell culture. Common specifications include 125 mL, 250 mL, 500 mL and 1000 mL, which can be selected according to experimental requirements and cell culture volume. Erlenmeyer flasks are usually made of PETG and PC (polycarbonate), of which PETG has better transparency and impact resistance, while PC provides higher heat resistance and chemical corrosion resistance.
There are two types of Erlenmeyer flasks: vent caps and plug seal caps. The vent caps use a 0.22μm filtration membrane, which is vent but not water-permeable. It allows air to circulate while effectively preventing microorganisms from entering. It is suitable for cell culture that requires oxygen exchange, while the plug seal caps can prevent the evaporation of culture medium and external contamination. They are usually used for long-term culture or experiments with high sterility requirements.
The bottom is usually divided into two designs: flat bottom and concave bottom. The flat bottom is suitable for low-speed and small-volume culture, providing stable and uniform liquid flow, and is suitable for shorter-term culture. The concave bottom design is more suitable for high-speed shaking and large-scale cell culture, promoting liquid circulation and cell suspension, and ensuring uniform cell growth and distribution under large-scale culture.
The above introduces the commonly used cell culture consumables. They play their own important roles in the cell culture process. We can view all Welso's cell products on the cell consumables page of this website. As a professional provider of cell consumables, we are committed to providing high-quality consumables to various laboratories, research institutes and universities around the world, helping scientific researchers to carry out every link of cell culture more smoothly and efficiently, and providing you with reliable solutions to make your experimental process more accurate and smooth.